For those who are even vaguely acquainted with music production and sound design, it is a known fact that a synthesizer is instrumental to create a musical track. Whether you are working in a professional studio or even in a home studio (view our guide of home studio essentials), no musical production is complete without a synthesizer. It is an instrument that allows you to produce a variety of different sounds and notes. A track that has been laid using a synthesizer is more dynamic and has a variety of different notes that come together to form a melody.
A synthesizer is an instrument that has popularly been used for music production since the 1970s and has since made it easier to set up a studio in the comfort of your home. Using a MIDI or Musical Instrument Digital Interface system, you can also covert the sounds of the synth into notes of other instruments. In other words, the notes you play on the synth can be converted back into guitar notes or even violin notes, using a MIDI system. The following is a brief guide to synthesizers. You will learn more about how they work and the many different types of synthesizers you can choose from.
How Do Synths Work?
Synthesizers have a few different components that come together to create that perfect sound. Most music composers and sound designers cannot do without a synthesizer. A synthesizer allows you to create a variety of different sounds even if you do not have other instruments at hand. If you connect your synthesizer to a MIDI or Musical Instrument Digital Interface system, you can compose entire tracks with just your synthesizer.
The following section will go through some of the basic components of a synthesizer that allow it to do what it does.

Oscillator
The oscillator is where the sound originates from. When you connect your synthesizer to a power source, the voltage from the source is able to oscillate electrons which generates waveforms. The sound you eventually hear is thanks to those waves. There are synthesizers with different types of waves as each pattern of the wave creates a different sound.
The synth’s oscillator is also where the pitch or the frequency is regulated. This refers to the speed of the vibration in which a waveform is able to complete one whole cycle. The frequency is assessed based on cycles per second, also known as Hertz. The faster the frequency is, the higher the pitch of the sound will be. In other words, with every double frequency, the pitch will go up an octave. The human ear is capable of hearing sounds in the range of 20 Hz and 20 kHz. So depending on the type of waveform you invest in and what the synthesizer is capable of creating, there is a vast array of sounds you can put together with a synthesizer!
Filter
The filter of the synthesizer is what is associated with the instrument’s timbre. The timbre, to put it in simpler terms, is the unique character of a sound or musical note. The sound is distinct from its pitch, which is why when you play the synthesizer and the violin at the same pitch, they will still sound different. This is because the timbre of both the sounds is unique. Each instrument plays around with harmonics. These are a group of frequencies that combine to provide a dominant pitch and a unique sound. When you hear it, you do not hear distinct pitches but only the overtone of those pitches that gives you a combined sound and a unique character, or timbre, for each sound. You can read more about harmonics here.
The filter section of the synthesizer is what modifies the timbre of the sound. The filter blocks certain frequencies and allows others in the waveform through. When this happens, you get a distinct sound that is created by combining certain frequencies. You can decide the kind of sound the filter will create by turning the filter knob and settling on the sound you want.
Amplifier
A synth also controls the size of the signal, which in turn is able to manipulate the volume. This is the job of the amplifier. But the amplifier is also able to modify the amplitude of the signal over time. It is not simply turning the volume knob but a strategic decision regarding how fast you want a signal to reach its peak volume and how long you would like it to sustain at that volume. These are all controls that the amplifier of the synth can employ with ease.

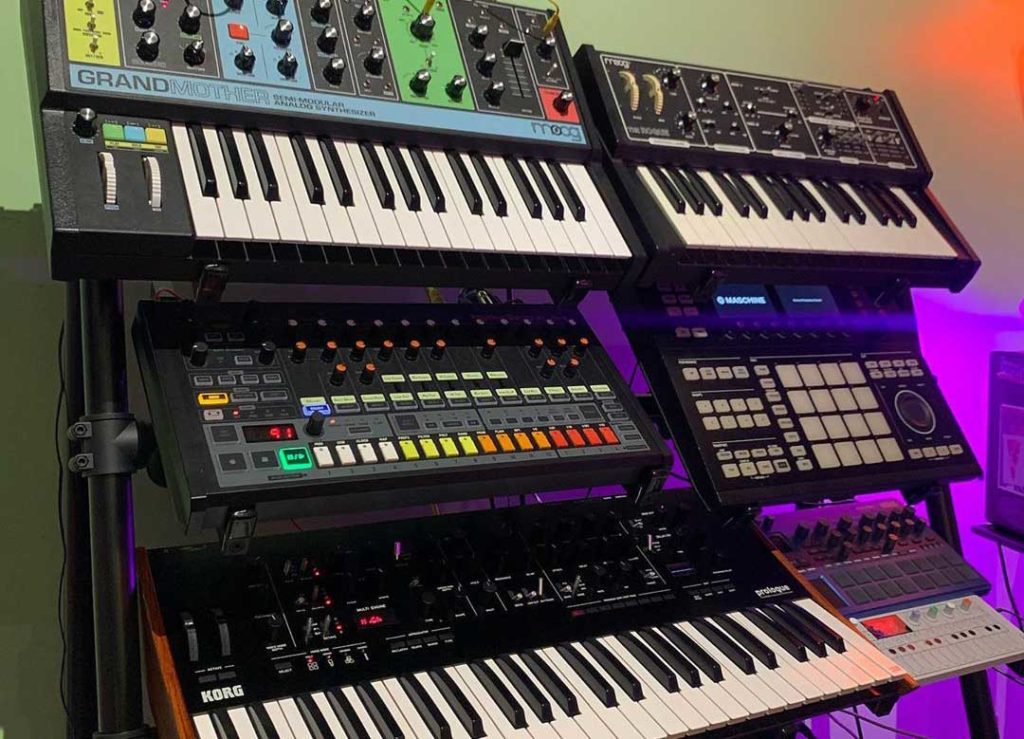
The envelope generator of the synth helps the amplifier manipulate the signal in this way. One of the most common and popular envelope generators is called the ADSR which is able to calibrate the onset of the sound, its fade and how long it can hold. It is also in charge of the release or the point where the sound ends.
Modulation
Like amplifiers and envelope generators, there are a few other modulators that work to manipulate the sound of the instrument. The low-frequency oscillator or LFO. This modulator is able to oscillate a signal even at extremely low frequencies. These frequencies are typically lower than what a human ear can hear but the sound that is created is not meant to be heard but is emanated to modulate other aspects of the sound. An LFO, when connected to the main oscillator, is able to create a vibration by wiggling the pitch (with its low-frequency sound). When it is attached to the amplifier, it is able to modulate the volume, creating a ‘tremolo’. When you apply it to the filter, you create the sound the signature dubstep sound called the ‘wobble bass’.
5 Best Synthesizers for 2021
Confused about which synth to buy? Poly, mono, analog or digital? We’ve reviewed the best synths for 2021.

Evolution of the Synthesizer
The synthesizer is an instrument that has come around only recently. While there are several instruments that modern-day musicians use which trace their origins to centuries back, the synthesizer is still an instrument whose origins can be more concretely documented. The simple reason for this being the fact that the synthesizer uses electricity.
It is unclear who the actual inventor of the synth is. There are a few contenders but it was at a time of technological inventions and discoveries in general, so a few different discoveries came together to create the instrument we recognize today.
However, Elisha Gray, an electrical engineer, is said to have accidentally discovered a preliminary version of the single-note oscillator around the late 19th century. The instrument was developed further and for a long time, it could only produce jarring sounds that could not be paired or associated with any other instrument (and, therefore, the synth was not used as a musical accompaniment for a long time)
It was only in the early 20th century that polyphonic (the ones that allow you to play multiple notes at once) began to be manufactured in Germany and in the United States. It is then that people began to acknowledge the instrument as something that would be conducive to musical production.

The musical industry owes the invention of the MIDI system to synthesizers. For a long time the instrument would be used as a secondary instrument for musical production, but by the 1970s, with radical changes in musical genres and the increasing popularity of electronic musical genres, especially synthpop, electro, dub and even disco, led to the synthesizer being recognized as a mainstream instrument that is essential to musical production.
Manufacturers began producing more portable and affordable versions of the synthesizer and the monophonic analog synthesizer also began to give way to the emergence of the digital, polyphonic ones, though these instruments may not necessarily be mutually exclusive. Yamaha and Roland became and continue to be some of the biggest and most sought after manufacturers of keyboards and synthesizers and no musical producer can now produce music without a keyboard, even if they are not producing electronic music. A synthesizer may be required to produce music of a variety of genres.
Even if the synth sound is not the most prominent in the track, it helps to manipulate the notes in the sound and makes musical production easier, yet more dynamic.
Different Types of Synthesizers
There are a few different types of synthesizers that you can pick from. All of these different types will either have minute differences in the sound or in the user experience. In the following section, you will be acquainted with a few different types of synthesizers and the features they have to offer. The different types we will be covering are:
- Analog vs Digital
- Monophonic vs Polyphonic
- Modular vs All-in-One
- Software vs Hardware
Analog vs Digital
The next section will go into detail about monophonic and polyphonic synthesizers, but in order to understand the difference between the two, it is important to know what analog and digital synthesizers are and how they are different from each other.
An analog synthesizer is one that relies on analog signals. Analog signals are those that have continuously-variable voltage in an analog circuit. These are complex circuits where for every increment in the signal level, there can be one level in between. This means that the number of levels in an analog circuit can be infinite.
Analog synthesizers were the first to appear when synths were being developed. The signal is generated and then modified directly in the electrical unit. This means that if you wanted to modulate your signal differently or do something new with the signal, you would need to change the circuits. Since this circuit is a more complex one, analog synthesizers tend to be a tad more expensive.
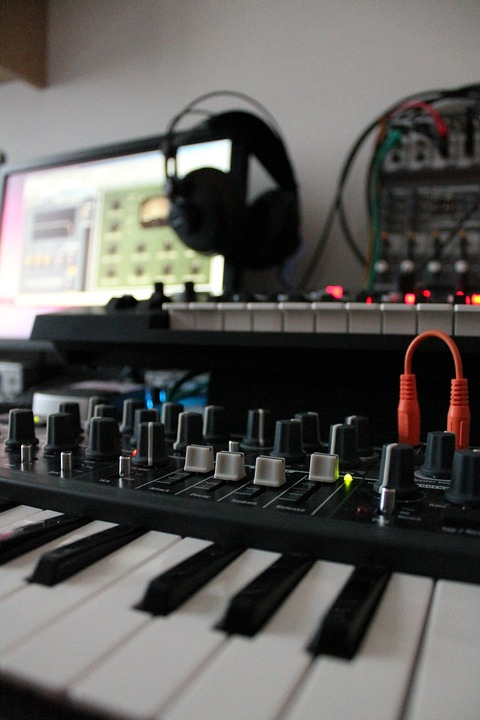

Digital synthesizers were developed later. The synthesizer creates digital sounds that are represented by corresponding numbers and relate to a discrete signal level. These digital numbers are then converted to an analog sound, which allows you to get the sound.
The digital synth system can store and process only finite numbers and signals. However, if you use enough numbers, the human ear will not be able to discern between the digital signal and the original analog signal it is trying to mimic.
Besides, you can create sounds on a digital system without changing the circuitry and you can reproduce identical sounds every time. They are also cheaper than their analog counterparts since the signals are finite and the circuit is less complex. But the sound of the analog synth is richer and larger since it is, after all, the original sound. What the digital synth reproduces is after the sound has been converted into an analog signal.
The difference is marginal, but to the trained ear, it is certainly there.
There are some synths that are hybrids and have managed to strike a balance between the two technologies. This means the signal path is analog but the circuitry is a simpler digital version.
Monophonic vs Polyphonic Synthesizers
The difference between a monophonic synthesizer and a polyphonic synthesizer, is in some ways, the distance between analog and digital synthesizers. When electronic synthesizers came about, most synthesizers were analog. This means that the synthesizers relied on an analog electrical signal for emanating sounds. This analog electrical signal requires a complex circuitry. These analog synthesizers are also recognized as monophonic synths. Since the circuitry is so complex, you can only play one note at once.
Naturally, after learning what a monophonic synthesizer is, you can ascertain the meaning of ‘polyphonic’ when you hear the term. A polyphonic synthesizer, as the name suggests, is one that allows you to play multiple notes at once. Most modern-day digital synthesizers are polyphonic as they do not require the complex circuitry of an analogous synth. Polyphonic synths, in many ways, are also less expensive than monophonic ones as they are a lot less complicated in terms of the circuitry.
But apart from this difference in versatility, there is also a difference in the kind of sound the two synths produce. Most keyboard and synth players seem to think the monophonic synthesizer has a more full sound. This is because the instrument is responsible for creating only that single note, so it is a lot richer and can be much larger. Since polyphonic synths have to create several notes at once, they are created keeping in mind a much thinner sound.
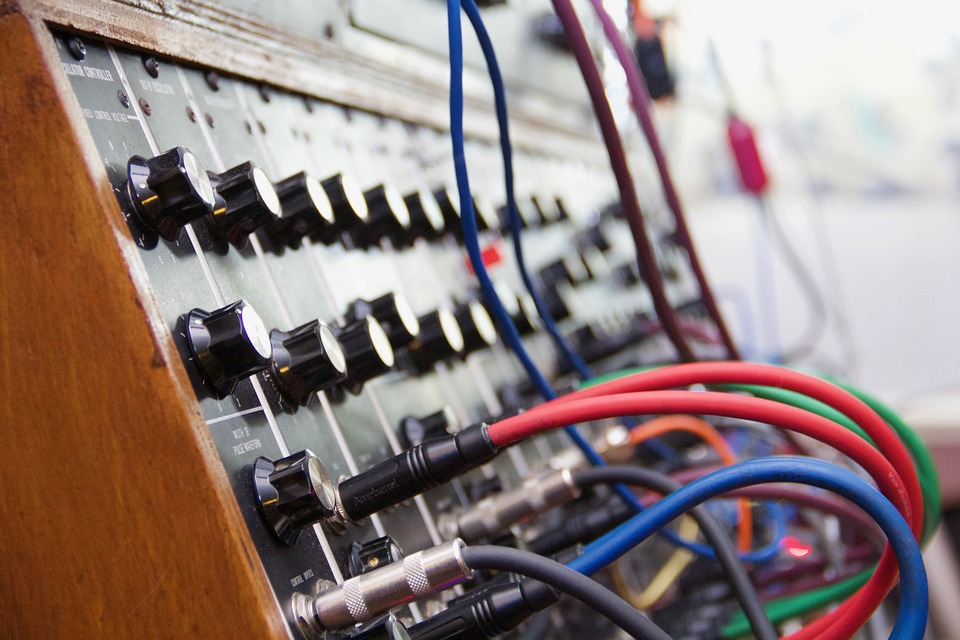
Which one you should buy depends on the intended purpose of the synthesizer. There are a few different questions you will need to consider. Like is this your first synthesizer? Will this be the main keyboard for your music production projects?
If the answer to these questions is yes, you may be happier and more confident with a polyphonic synthesizer. They are typically cheaper and can give you a wider range of sounds that you can produce. But if the synthesizer is a supplementary one that you want to use to make the sounds you are creating richer, you can opt for a monophonic one. It does not have to be your main synthesizer, but every now and then if you are looking to strike a larger note to make your musical production richer, a monophonic synthesizer is perfect for that.
Modular vs All in One
As has been described in the sections above, there are several different components that come together to make a synthesizer work. In a modular synthesizer, all the components are placed separately on a mounted rack. The components can be moved around physically and they can be placed wherever you think it is more comfortable to have them.
In a modular synthesizer, there is no default signal routing. Each module needs to be physically connected to the other modules using patch cables. This gives you a great deal of freedom as you can create very unique and new sounds. There are very few rules about which modules that can be patched to which ones so you really do have a lot of freedom when it comes to using a modular synthesizer. The modules are not even attached to a keyboard!
In comparison, an all-in-one synth has all the components integrated inside their case. You do not have the freedom to patch different modules and create your own sound. Regardless of whether you are using an analog synth, where you conduct the patching through switches and knobs, or the modern-day digital keyboards, where you pick a preset to get started, these are all examples of all-in-one synths that are navigated radically differently from modular synthesizers.

Modular synthesizers may actually be a better option if you are learning to use the keyboard or are inclined to experiment with the sounds. By trying out different permutations and combinations of patching the modules, you will get to see exactly how the signal behaves and where it goes. This gives you a better musician and accords you with a great deal of flexibility!
Software vs Hardware Synthesizers
Now, this is a curious type of synthesizer or at least it sounds like it. A synthesizer is an instrument so naturally, it comes in the hardware form. Where is the question of software? Actually, with the advance of digital technology, you can also purchase a synthesizer that exists only digitally and not physically. Software synthesizers, or soft synths, exist completely inside the computer! This is the turn that technology has taken that you only need to load a program into your computer and you will have a fully functional synth in front of you to create your music! They are typically designed to emulate hardware synths as faithfully as possible.
Hardware synths may also be quite close to soft synths. Some hardware synths are also small units with specialized computers attached to a keyboard. These hardware synths also have controls that are software assignable, though hardware synths can be both analog and digital.
5 Best Vocoder/Speech Synthesizers [Reviews & Buyer’s Guide]
Looking to add a little funk to your music? Check out our rundown on the top 5 best vocoders/speech synthesizers.

What Should a Beginner Keep in Mind While Buying a Synthesizer?
If you are a beginner, one of the most important things to keep in mind before buying a synthesizer is the intended purpose of the instrument.
The types of synthesizers that have been described above are not necessarily mutually exclusive.
A monophonic synthesizer may also be an analog synthesizer, even while being an all-in-one synthesizer.
But the following are a few notes that may help you make a better choice:
- If your intention is to learn how to play the synthesizer or to better your skills, you may be better off with a synthesizer that is more versatile and will give you greater flexibility to learn.
- A modular synthesizer may be a great device to learn more about the instrument from, the learning curve can be quite steep.
- An all-in-one synthesizer will be much easier to play but you may not learn as well as with a modular synthesizer.
- But a modular synthesizer is perhaps better suited to intermediate level users and not complete novices.
- If you are looking for the main keyboard that will aid you in most of your music production, a polyphonic synthesizer will be a much better choice.
- Once you have gained some experience with music production, you can add a monophonic synthesizer as a supplementary instrument.
Final Thoughts
A synthesizer is a beautiful and versatile instrument that has completely changed how music is produced around the world.
It has managed to make music production a lot more efficient and streamlined and has given composers greater control over the sounds they can create. The technology has advanced so much that you can install an entire keyboard on your computer and do not even require any hardware to play it.
No matter what genre of music you are inclined to produce, a synthesizer can make the process a lot more efficient and simple. Even if you are a classical musician and prefer not to have electronic sounds in your music, you would perhaps still acknowledge the importance of a synth in music production. It is an intricately designed instrument that has a number of processes that come together in strategic ways to create a sound. With a synthesizer, a musician is really able to grasp the science and the physics behind creating a sound.
It takes a sharp bend of mind and a lot of precision to get the perfect melody and a synthesizer is the embodiment of that.




![5 Best Vocoder/Speech Synthesizers [Reviews & Buyer’s Guide] Roland's Best Vocoder](https://homestudiohub.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/null-8-218x150.jpeg)




![5 Best Electric Pianos Under $1000 [Reviews & Buyer’s Guide] best electric piano under $1000: Casio PX160BK 88-Key Digital Piano](https://homestudiohub.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/03/null-15-80x60.jpeg)



